The Role of Ocean Data in Climate Modeling
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Climate Modeling and Ocean Data
- What is Climate Modeling?
- The Importance of Ocean Data in Climate Modeling
- Key Components of Ocean Data for Climate Modeling
- Ocean Temperature Data
- Sea Level Measurements
- Ocean Currents and Flow Patterns
- How Ocean Data Influences Climate Predictions
- Role of Ocean Data in Weather Forecasting
- Ocean Data and Long-Term Climate Projections
- Ocean Data in Predicting Extreme Climate Events
- The Role of Ocean Data in Hurricane Predictions
- Using Ocean Data for Sea Level Rise Projections
- Integrating Ocean Data with Other Climate Variables
- Combining Ocean Data with Atmospheric Data
- The Future of Ocean Data Integration
- Conclusion: The Growing Role of Ocean Data in Climate Modeling
Introduction to Climate Modeling and Ocean Data
Climate modeling plays a critical role in our understanding of how the Earth's climate behaves, both today and in the future. It helps scientists predict weather patterns, track global temperature changes, and even predict extreme weather events. Climate models rely on large sets of data, and one of the most crucial sources of information is ocean data in climate modeling.
Ocean data provides insights into ocean temperatures, currents, and sea levels all of which influence climate. The vast oceanic expanse covers 70% of the Earth’s surface and acts as a massive heat sink. But how does ocean data tie into climate modeling? Let’s break it down.
What is Climate Modeling?
Climate modeling involves using mathematical representations of Earth's climate systems to simulate past, present, and future climate conditions. Scientists build models that incorporate variables such as temperature, wind patterns, atmospheric composition, and ocean data. These models are used to forecast climate changes and predict the effects of various scenarios, including greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation.
By running simulations with these models, scientists can explore how different variables, such as rising CO2 levels or melting ice caps, impact global temperatures and weather patterns. The more accurate the data fed into the models, the more reliable the predictions will be.
The Importance of Ocean Data in Climate Modeling
Oceans play a huge role in regulating Earth's climate, which is why oceanographic data is so essential in climate modeling. For instance, oceans absorb about 90% of the excess heat from global warming, preventing much of it from impacting land areas. By analyzing ocean data, scientists can gain insights into how oceans are influencing climate change, including the warming of the Earth’s atmosphere and the shifting of weather patterns.
Without accurate ocean data, climate models would lack critical information about how heat is distributed across the planet. This could lead to less reliable predictions about global warming, sea level rise, and even the frequency and intensity of storms.
Key Components of Ocean Data for Climate Modeling
Ocean data encompasses various types of measurements that provide insight into the health and movement of the ocean. The following are the key components of ocean data collection that scientists use in climate models:
- Ocean Temperature Data
- Sea Level Measurements
- Ocean Currents and Flow Patterns
Ocean Temperature Data
Ocean temperature plays a critical role in regulating the global climate. Water absorbs heat from the sun, and changes in ocean temperature can affect the Earth’s heat balance. For example, when sea surface temperatures rise, it can influence the intensity and path of tropical storms or hurricanes. By tracking temperature trends across the oceans, scientists can better understand global temperature fluctuations and their effects on climate patterns.
Ocean temperature data also helps us understand ocean and climate interaction such as how heat is exchanged between the ocean and the atmosphere. This is essential for accurate climate projections and understanding long-term trends in climate change.
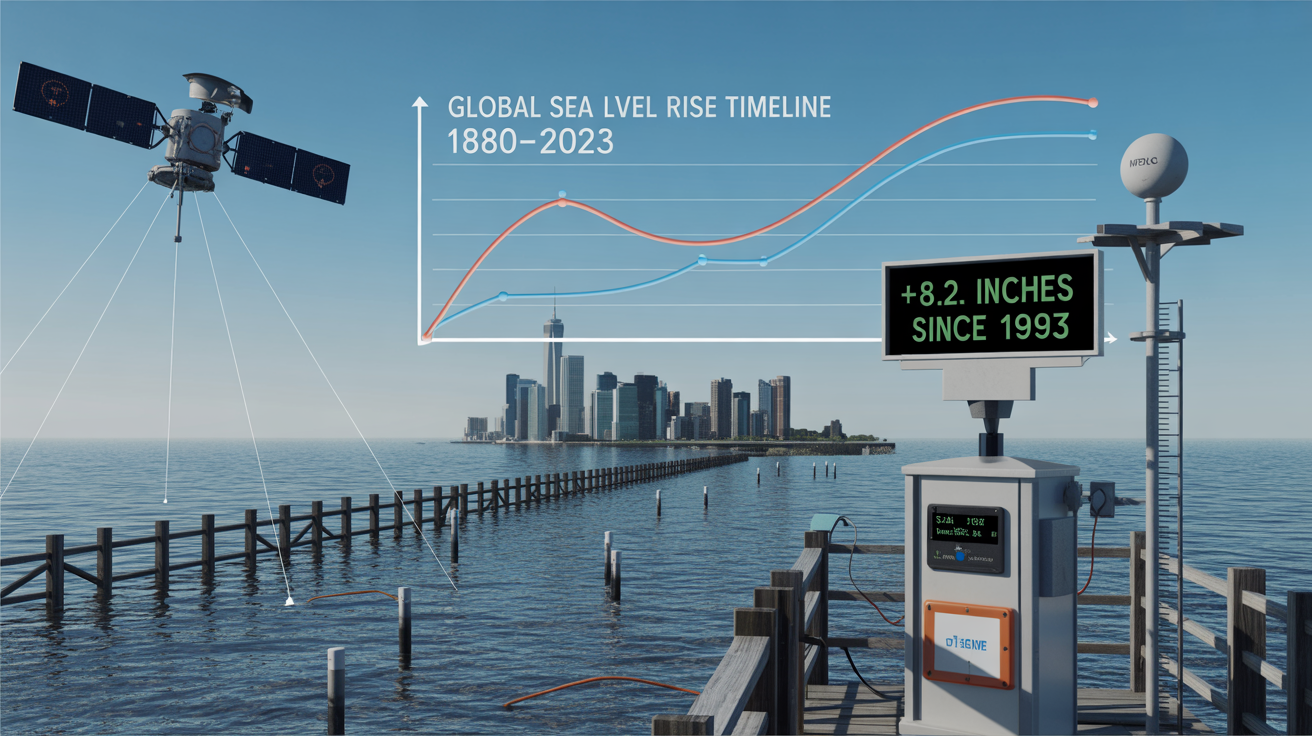
Sea Level Measurements
Rising sea levels are one of the most visible impacts of climate change, and they are largely influenced by the warming of the oceans. As the ocean warms, water expands, and polar ice caps begin to melt, both of which contribute to rising sea levels. Accurate sea level measurements are essential for climate models, as they help scientists predict future flood risks, coastal erosion, and other consequences of sea level rise.
These measurements are taken through satellite observations and tide gauges, providing crucial data for forecasting the impacts of climate change on coastal communities.
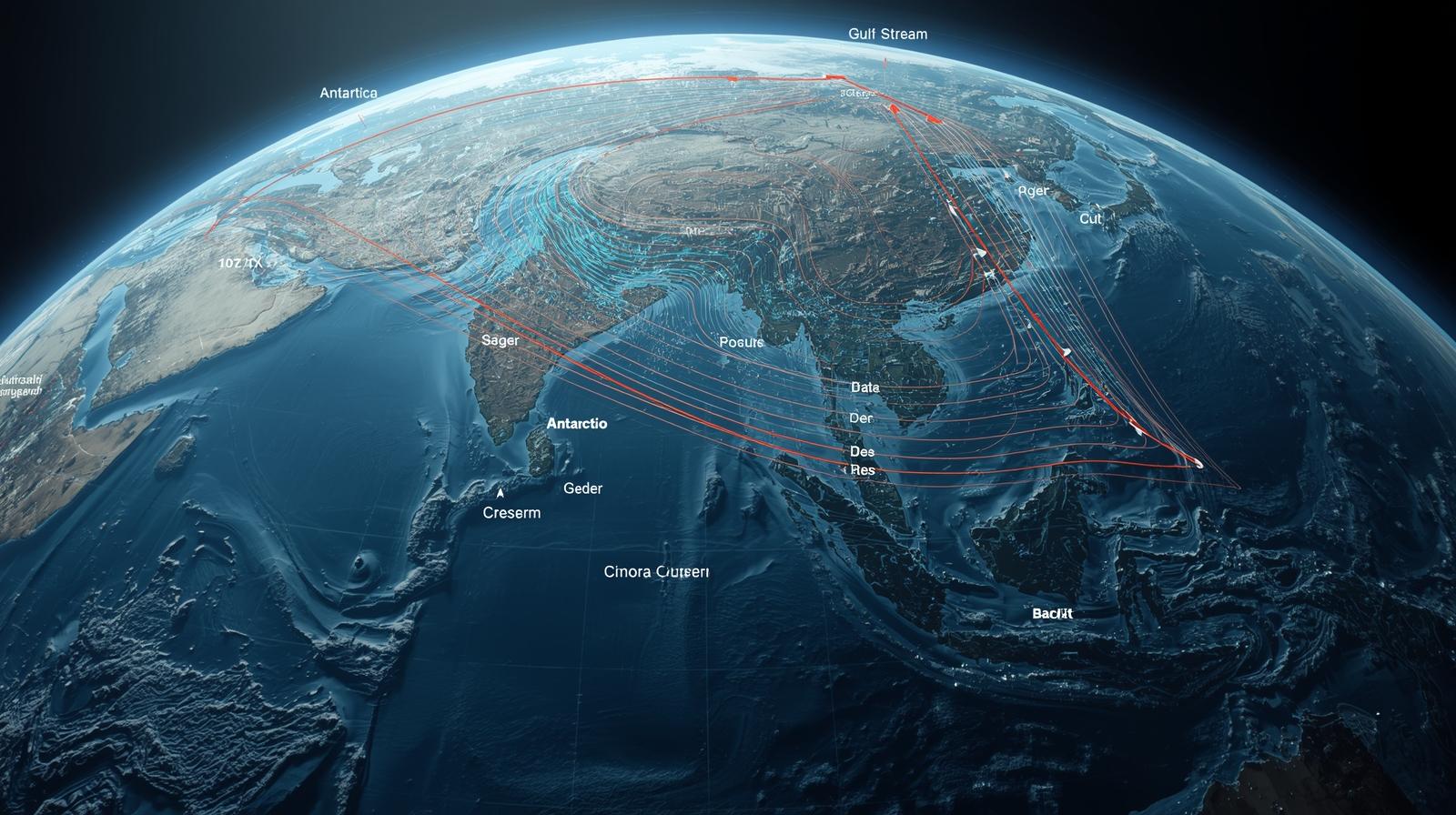
Ocean Currents and Flow Patterns
Ocean currents move vast amounts of water around the globe, distributing heat and nutrients. These ocean currents play a huge role in regulating the Earth's climate. For instance, warm currents like the Gulf Stream help moderate temperatures in Europe, while cold currents like the Antarctic Circumpolar Current help regulate temperatures in the Southern Hemisphere. Understanding how ocean currents shift with climate change can help scientists predict changes in regional climate patterns, such as droughts or extreme weather events.
How Ocean Data Influences Climate Predictions
Ocean data is instrumental in making reliable climate predictions. By incorporating oceanic measurements into climate models, scientists can simulate more accurate climate forecasts and improve environmental forecasting.
Role of Ocean Data in Weather Forecasting
Ocean data is critical for weather forecasting. For example, scientists use sea surface temperature data to predict phenomena like El Niño and La Niña, which can drastically alter weather patterns across the globe. Changes in ocean temperatures can influence the strength and frequency of storms, rainfall patterns, and droughts. By analyzing these patterns, meteorologists can make more accurate short-term weather forecasts.
Ocean Data and Long-Term Climate Projections
For long-term climate projections, ocean data helps predict how the Earth's climate will evolve over the coming decades or centuries. As oceans absorb large amounts of heat and CO2, they can buffer the full effects of climate change, but only up to a point. By studying ocean data, scientists can project how rising temperatures, acidification, and sea-level rise will affect the global climate in the future.
Ocean Data in Predicting Extreme Climate Events
Extreme climate events, such as hurricanes, floods, and extreme heat waves, are becoming more frequent as a result of climate change. Ocean data plays an important role in predicting and understanding these extreme events.
The Role of Ocean Data in Hurricane Predictions
Hurricanes are fueled by warm ocean waters, and understanding how ocean temperatures impact storm formation is essential for predictive modeling. Scientists use ocean temperature data to predict when and where hurricanes are likely to form and how intense they may become. This data is also crucial for evacuations and disaster preparedness in vulnerable coastal regions.
Using Ocean Data for Sea Level Rise Projections
Sea level rise is one of the most devastating effects of global warming. Ocean data helps scientists predict the rate of sea level rise and the potential impacts on low-lying areas. By monitoring changes in ocean temperatures and the melting of polar ice, scientists can make more accurate projections of future sea level rise and the potential consequences for coastal cities and ecosystems.
Integrating Ocean Data with Other Climate Variables
Climate models are only as accurate as the data fed into them. Integrating ocean data with other variables, such as atmospheric measurements and greenhouse gas levels, is essential for creating comprehensive climate simulations.
Combining Ocean Data with Atmospheric Data
To improve the accuracy of climate models, scientists combine ocean data with atmospheric data such as CO2 levels, cloud cover, and air temperature. This integrated approach allows for a more complete picture of the Earth's climate system, improving both short-term weather forecasts and long-term climate predictions.
The Future of Ocean Data Integration
The future of ocean data integration lies in combining more types of data from a variety of sources, including satellites, ocean buoys, and underwater sensors. As technology advances, we will have more real-time ocean data to feed into climate models, enabling us to make faster and more accurate predictions. This could improve our understanding of ocean-atmosphere interactions and provide us with better tools to address climate change.
Conclusion: The Growing Role of Ocean Data in Climate Modeling
In conclusion, ocean data in climate modeling plays an essential role in understanding and predicting the impacts of climate change. The ocean’s vast expanse, temperature trends, sea level changes, and current patterns all contribute to regulating the Earth's climate. By collecting and analyzing oceanic measurements, scientists can improve climate predictions, forecast extreme weather events, and better prepare for the challenges ahead. As climate change accelerates, the integration of ocean data into climate models will only become more critical.
Learn More About Ocean Data and Its Role in Climate Modeling
FAQs
1. Why is ocean data important for climate modeling?
Ocean data is crucial because it provides insights into how oceans regulate temperature, sea levels, and weather patterns, all of which influence global climate.
2. How do ocean currents affect climate predictions?
Ocean currents distribute heat around the globe, impacting regional climates and influencing the intensity of storms and precipitation patterns.
3. What role do oceans play in global warming?
Oceans absorb excess heat and CO2, buffering the effects of global warming but also contributing to sea level rise and changing climate patterns.
4. How does ocean temperature data help predict extreme weather?
Warmer ocean temperatures fuel extreme weather events like hurricanes, and ocean temperature data helps scientists predict the timing and intensity of these storms.
5. How do ocean currents affect weather forecasting?
Ocean currents influence regional weather patterns, such as precipitation and temperature, and are essential for accurate short-term weather forecasts.
6. What is the biological pump and how does it relate to climate change?
The biological pump refers to the process by which marine organisms absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, helping to regulate carbon levels and mitigate climate change.
7. How does ocean data affect long-term climate projections?
By studying ocean data, scientists can predict future sea level rise and other long-term climate trends, improving long-term climate projections.
8. How does ocean data help in predicting sea level rise?
Ocean data helps track temperature changes and melting ice caps, which are the primary drivers of sea level rise due to global warming.
9. Why is ocean data combined with atmospheric data for climate models?
Combining ocean and atmospheric data gives a more complete picture of the Earth’s climate system, improving the accuracy of climate models.
10. What technological advancements are improving ocean data collection?
Advancements in satellite technology, ocean buoys, and underwater sensors are providing more real-time ocean data, enhancing climate predictions.